THE MANY FACES OF COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms an abnormal inflammatory response in the lungs usually caused by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases. The most common respiratory symptoms include dyspnea, cough and/or mucus hypersecretion.
Global burden of COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world and is estimated by the WHO to become the 3rd leading cause of death by 2020. The COPD burden is expected to increase in coming decades because of continued exposure to COPD risk factors and aging of the population. More than 3 million people die of COPD every year accounting for 6% of all deaths globally. COPD therefore represents an important public health challenge.
COPD is a significant economic burden to the healthcare system. The total direct costs of respiratory disease are estimated to make up 6% of the total healthcare budget in the European Union, with COPD accounting for 56% of the cost of respiratory diseases.

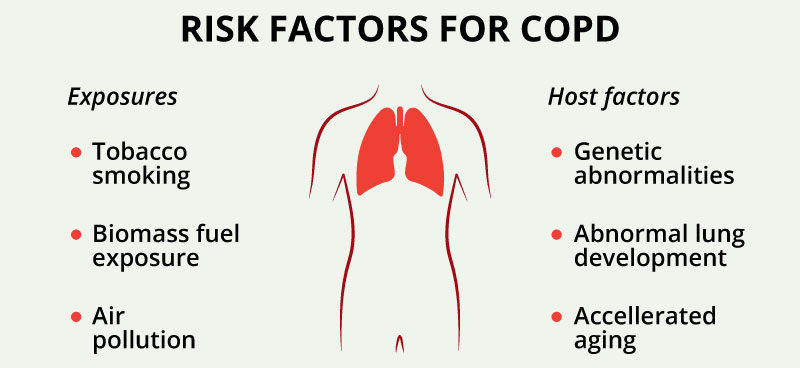
Risk factors for COPD
The main risk factor for COPD is tobacco smoking but other environmental exposures such as biomass fuel exposure and air pollution may contribute. Besides exposures, host factors predispose individuals to develop COPD. These include genetic abnormalities, abnormal lung development and accelerated aging.
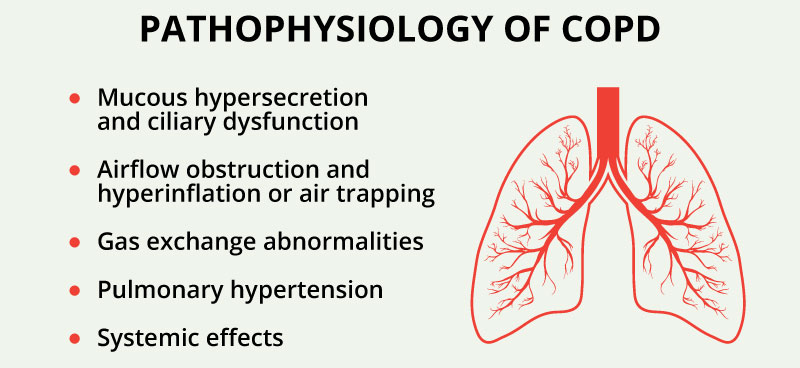
Pathophysiology of COPD
COPD is characterized by poorly reversible airflow obstruction and an abnormal inflammatory response in the lungs. Innate and adaptive immune responses to long-term exposure to noxious particles and gases, particularly cigarette smoke may result mucous hypersecretion and ciliary dysfunction, airflow obstruction and hyperinflation, gas exchange abnormalities, pulmonary hypertension and systemic effects.
Patients with COPD may experience periods of acute worsening of respiratory symptoms, acute exacerbation of COPD (AE-COPD), a leading cause of ICU admissions and associated with a high mortality. Exacerbations are often associated with increased inflammation and may be triggered by an infection with bacteria or viruses or by environmental pollutants. AE-COPD often requires ventilator support.
From the Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2017. Available from: http://goldcopd.org